April 12, 2020
The Case for Autonomous Banking

Just a few years ago, the concept of autonomous banking, like the concept of autonomous vehicles, would have seemed like an idea taken out of a futuristic, incomprehensible sci-fi novel.
Yet, anyone aware of customers’ and tech trends in the financial industry would be hard-pressed to argue that the rapid advances in technology have not only made “self-driving finance” a not-too-distant reality but are also serving as the impetus to reevaluate how banks and customers, alike, approach financial services.
In a recent report, Forrester defines Autonomous Banking as “algorithm-driven services that make financial decisions or take action on a customer’s behalf”.
The Reasons for Banks to Embark on the Journey Toward Self-driving finance are clear:
- Customers Need Help Making Better Financial Decisions – In 2019, alone, 35% of US adults said they feel anxious about their finances, while 32% said they are living from paycheck to paycheck.
- Customers are Gaining More Trust in Automated Financial Services – A majority of US adults are increasingly trusting algorithms over human beings, with one in five people believing that computer algorithms can make sound financial decisions on their behalf.
- Customers are Adopting Autonomous Services that Reinvent Traditional Financial Products – While fintech startups are using automation for nearly every aspect of banking, incumbent financial institutions are similarly rolling out automated services to better help customers manage their finances.
Automating financial services, however, does not only help customers – it helps banks, by boosting customer engagement, acquisition and retention, as well as up-sales and cross-sales, and ultimately the bank’s ROI and bottom line.
Personetics AI-Based Personalized Engagement Platform’s capabilites are circled in red.
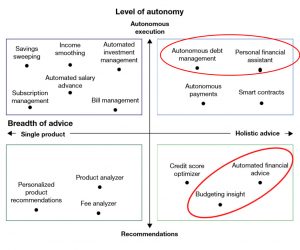
Reference: The Dawn of Autonomous Finance, March 18,2020
The Four Stages Toward Achieving Autonomous Finance
- Data – Data enrichment and categorization are the most basic and fundamental elements of the first stage toward achieving automated finance. These services –typically offered by traditional, “cookie cutter” Personal Financial Management (PFM) tools — are essential elements that more sophisticated platforms can build upon to advance to more mature stages of autonomous finance.
- Insights – The next stage is when banks offer personalized financial “insights” or stand-alone bite-sized information about a customer’s financial activity. For example, an autonomous bank can proactively alert customers when they have enough money in their checking account to transfer over into their savings account, when they should be saving for an unexpected expense that is due the following month or when they might be paying double for subscription-based services.
- Advice – After establishing a deeper understanding of their consumers, financial institutions can apply the next level of self-driving finance to generate personalized advice. This proactive advice gives customers a “heads up” to take action based on the insights received and rectify issues before they become problems. By giving customers automated advice based on their financial data, transactions and behaviors, banks can help customers achieve their financial goals, such as boosting savings or paying down debts.
- Automation – After understanding customers in a deeply personalized way, financial institutions will be able to take action on behalf of their customers, with little to no daily intervention from the customer. Autonomous banking wellness programs will find savings across multiple customer accounts, protect against overdraft, and even pay off prioritized debts when excess funds are available.
Forrester frames the journey toward achieving autonomous finance in slightly different terms, saying that autonomous finance will evolve through four levels of maturity:
- Level 1 – Specific actions are automated, but only as directed by a human, such as recurring transfers.
- Level 2 – Entire tasks, involving multiple actions, are automated, but the human is asked to intervene under certain circumstances.
- Level 3 – Most aspects of a customer’s financial life are automated, including where their money is stored, how it is allocated and which firms are used for transactions. In this stage, customers are still asked to take over when it comes to major financial decisions, such as retirement plans and debt management solutions.
- Level 4 – Customers’ entire financial lives are managed by a small number of providers that automatically make decisions and act based on the customer’s best interest, as well as current and anticipated needs.
The Goals of “Self-Driving Finance”
The goal at every level of financial automation is to enable the customer to better manage their finances and help them reach their financial goals and needs by providing automated or semi-automated financial data driven capabilities.
However, it cannot be overstressed that the benefits of automated autonomous finance are not limited to customers. Banks and credit unions that strategically embrace self-driving finance will see a meaningful increase in ROI, with higher customer satisfaction, increased digital engagement and growth in new accounts. In addition, banks will quickly achieve market differentiation and smart, proactive and agile capabilities.
Want to explore how your bank can harness the power of AI to engage and serve customers? Request a demo now
Latest Posts

The AI Implementation Reality Check

Why Asia Pacific Pacific Banks Must Lean into Cognitive Banking: A Conversation with Dr. Dennis Khoo

Explore our Spring Release Highlights – From Integrated Marketing Offers, to Custom Trackers, and AI Innovation